What are Single Layer PCBs?
In the ever-evolving world of electronics, single-layer printed circuit boards (PCBs) have emerged as a versatile and cost-effective solution for a wide range of applications. As the name implies, these boards feature conductive traces on only one side of an insulating substrate, offering a simple yet efficient design.
Single layer PCBs stand in contrast to their multi-layered counterparts, which consist of two or more layers of circuitry stacked together. While multilayer PCBs cater to more complex and dense designs, single-sided PCBs excel in applications where simplicity, affordability, and low component density are key requirements.
The primary advantage of single layer PCBs lies in their straightforward layout and routing process. With components and traces confined to a single plane, the design and manufacturing complexities are significantly reduced. This simplicity translates into lower production costs, making single layer PCBs an attractive choice for cost-sensitive projects, prototyping, educational purposes, and hobbyist electronics.
Despite their inherent limitations in accommodating high-density circuits, single layer PCBs continue to find widespread use in consumer electronics, testing platforms, and low-complexity applications where their unique advantages outweigh the need for advanced multilayer designs.
This comprehensive guide delves into the different types of single layer PCBs, their distinct characteristics, and their suitability for various applications. From rigid to flexible, metal-core to ceramic, explore the diverse range of single-sided PCB options and unlock their potential in your next electronic endeavor.
In the subsequent sections, we will uncover the key features, advantages, and ideal use cases for each type of single layer PCB, enabling you to make informed decisions and leverage the simplicity and cost-effectiveness they offer.
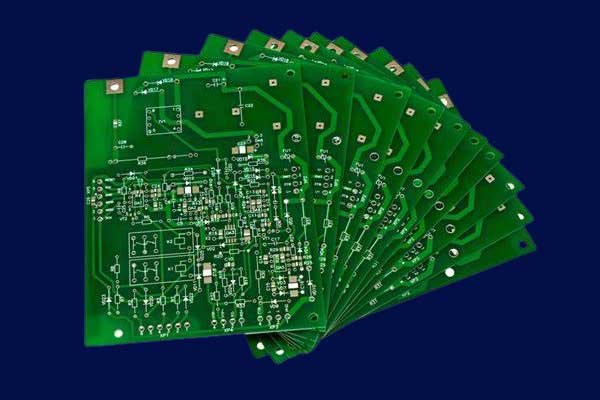
Main Types of Single Layer PCBs
Through the diverse range of single layer PCB types, designers can select the optimal board material and construction suited for their specific requirements in terms of thermal management, flexibility, durability, and operating conditions. Whether it’s the rigid yet economical fiberglass boards, the bendable polyimide flex PCBs, or the thermally conductive aluminum core variants, single-sided designs offer tailored solutions across industries.
Explore the unique attributes that define each prominent single layer PCB type, unlocking new possibilities for your next electronic product or application. From prototypes to specialized high-power designs, these single-sided boards provide a versatile foundation for circuit manufacturability, reliability and performance.
Maybe you also like:
Types of PCBs: Comprehensive Guide to Printed Circuit Boards
Single layer rigid PCBs are the most commonly used type of single-sided printed circuit boards. As the name suggests, these PCBs are manufactured using rigid materials like fiberglass or epoxy resins, giving them an inflexible and sturdy form factor.
These robust single layer PCBs are designed to maintain their shape and structural integrity, making them ideal for applications where the board needs to support and secure other components. Computer motherboards, televisions, and various other consumer electronics frequently employ single layer rigid PCBs as their core circuitry foundation.
One of the key advantages of single layer rigid PCBs is their durability and resilience against mechanical stresses. The rigid substrate material ensures the board can withstand vibrations, impacts, and other physical forces encountered in industrial or commercial settings.
Despite being confined to a single conductive layer, rigid single-sided PCBs offer ample design real estate for layouts with moderate component density. Their simplicity streamlines the manufacturing process, contributing to cost-effectiveness for projects with budgetary constraints.
Whether you’re developing a prototype, assembling educational electronics kits, or mass-producing consumer goods, single layer rigid PCBs provide a reliable and economical solution for your circuit design needs, excelling in applications where ruggedness and affordability are paramount.
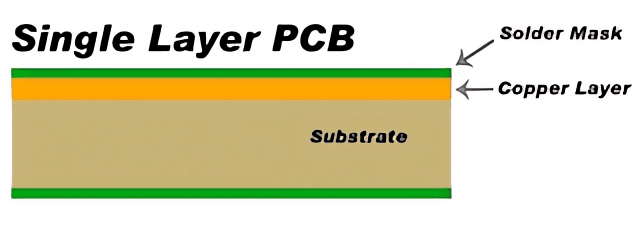
Single Layer Flexible PCBs - Bending to Your Design Needs
Defying the rigid constraints of traditional PCBs, single-layer flexible printed circuit boards introduce a new dimension of versatility to electronic designs. As their name implies, these unique boards are constructed from flexible plastic-based materials that can bend, twist, and conform to various shapes without compromising functionality.
At the core of single layer flex PCBs lies a polyimide substrate, renowned for its remarkable flexibility and heat resistance. This advanced polymer material allows the conductive traces to remain intact and operational even when bent to extreme angles or flexed repeatedly. Such durability makes single layer flexible PCBs an ideal choice for applications where space is limited, and a rigid board simply won’t fit or cannot accommodate the required movements.
One of the key advantages of these single-sided flexible boards is their ability to seamlessly integrate into compact and ergonomic product designs. From wearable devices and medical equipment to industrial machinery and aerospace components, single layer flex PCBs enable circuit placement in previously inaccessible areas, unlocking new possibilities for innovation.
Moreover, their lightweight and thin profile contribute to overall weight and space savings, crucial factors in industries like aerospace, where every gram counts. The elimination of bulky connectors and the direct integration of flexible circuits streamline the assembly process, further enhancing cost-effectiveness.
While single layer flexible PCBs may have limitations in terms of component density and thermal management compared to their rigid counterparts, their unique form factor opens up a world of possibilities for designers seeking to combine electronics with intricate mechanical structures or ergonomic designs.
Whether you’re developing a next-generation wearable device, a compact medical diagnostic tool, or a space-constrained industrial control system, single layer flexible PCBs offer a ingenious solution, merging cutting-edge electronics with exceptional flexibility and adaptability.
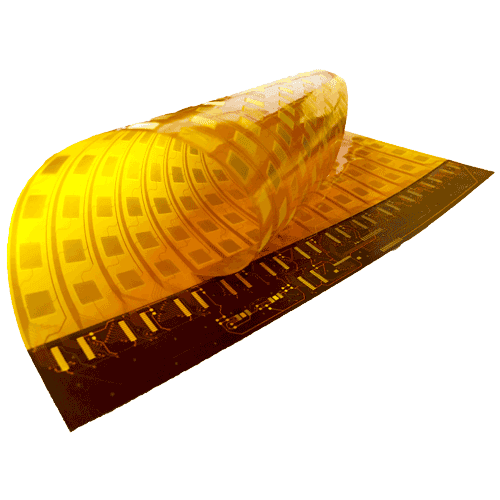
Single Layer Aluminum PCBs - Superior Thermal Performance
In high-power or heat-intensive electronic applications, traditional PCB materials often struggle to meet stringent thermal management requirements. This is where single layer aluminum PCBs (or aluminum-based PCBs) come into play. This unique type of PCB utilizes a solid aluminum metal base as the core substrate, endowing it with exceptional heat dissipation capabilities.
Aluminum is renowned for its excellent thermal conductivity properties. Single layer aluminum PCBs can rapidly transfer and dissipate heat from the component and trace layers. Compared to conventional FR-4 and polyester substrates, the metal aluminum core can much more efficiently conduct heat away from hot spots to the entire board surface for convection cooling. This advantage makes single layer aluminum PCBs an ideal thermal solution for LED lighting, power converters, and other high-power electronic products.
Beyond their superior thermal management, single layer aluminum PCBs offer several other distinct advantages. The solid aluminum core is both lightweight and robust, providing excellent structural strength and vibration resistance. They also exhibit superior electromagnetic shielding capabilities, effectively blocking electromagnetic interference from sensitive circuitry. Furthermore, aluminum PCBs demonstrate corrosion resistance and high-temperature resilience.
Applications for single layer aluminum PCBs span LED luminaires, inverters, industrial machine controls, aerospace systems, and more. Whether it’s high-power LED arrays or high-speed servo motors, heat dissipation is critical to ensuring reliable operation and preventing overheating failures. Leveraging the rapid heat transfer of single layer aluminum PCBs, thermal designs for such devices can be more efficient and compact.
Of course, single layer aluminum PCBs do have some limitations. Due to having only a single routing layer, component density and trace routing flexibility are restricted. Additionally, the manufacturing process for aluminum-based boards is relatively complex, resulting in higher costs compared to traditional PCBs. However, for applications with stringent thermal and structural demands, sacrificing some layout space for superior heat dissipation is often a worthwhile trade-off.
Overall, single layer aluminum PCBs, with their exceptional thermal management capabilities, robust metallic nature, and superior electromagnetic shielding, provide a high-performance and reliable solution for high-power density electronic products, driving innovation across various industries.
Related Reading:
- Aluminum PCBs: The Optimal Thermal Solution for High-Power Electronics
- Applications of Aluminum PCB: A Comprehensive Overview
- The Ultimate Guide to Aluminum PCB Manufacturing Process
- The Importance of Choosing the Right Aluminum PCB Manufacturer
- Comparative Analysis of Aluminum PCB and FR-4 PCB
- Multilayer Aluminum PCB Introduction and Manufacturing
- 2 Layer, Double Sided Aluminum PCB Manufacturing Service
- Hybrid Aluminum PCB Manufacturing Services
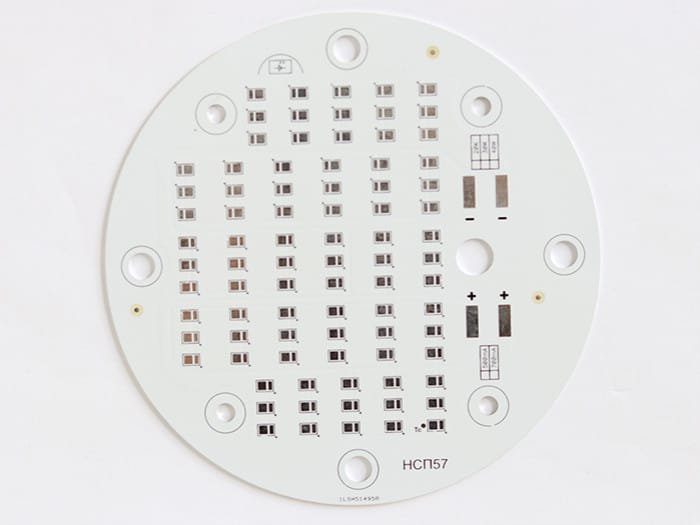

Single Layer Ceramic PCBs - Unrivaled High-Temperature Endurance
In certain extreme operating environments, traditional PCB materials like FR-4 and polyester often fail to meet stringent requirements. This is where single layer ceramic PCBs come into play. This specialized type of PCB utilizes ceramic as the base substrate material, endowing it with exceptional high-temperature capabilities and superior insulation properties.
Ceramic inherently possesses outstanding thermal stability and heat resistance. Single layer ceramic PCBs can continue to operate reliably in extreme high-temperature conditions without suffering the material softening or thermal expansion issues that plague conventional PCBs. Their operating temperatures can reach up to 300°C or even higher, making them ideally suited for harsh thermal environments in aerospace, automotive, industrial furnaces, and more.
Beyond their unparalleled high-temperature performance, single layer ceramic PCBs offer several other unique advantages. They exhibit excellent corrosion and chemical resistance, able to withstand the attacks of acidic, alkaline, and saline corrosive media. Additionally, the ceramic substrate provides outstanding insulation performance and electromagnetic interference shielding capabilities to the PCB.
While primarily utilized in specialized high-temperature application scenarios, the performance benefits of single layer ceramic PCBs have also found use in other industries. Medical devices, oil and gas exploration equipment, and more have leveraged these durable boards.
At the same time, single layer ceramic PCBs do have some limitations. First, the manufacturing process for ceramic substrates is relatively complex, leading to higher costs for these PCBs. Secondly, compared to traditional PCBs, single layer ceramic boards offer lower component density and less usable space. Furthermore, in certain extreme high-temperature situations, thermal mismatch issues with the traces need to be carefully addressed.
Overall, with their unrivaled high-temperature endurance, superior insulation properties, and corrosion resistance, single layer ceramic PCBs provide a reliable solution for electronic devices operating in the most demanding environments. They serve as a robust backbone, ensuring critical systems can continue stable operation under extreme conditions.
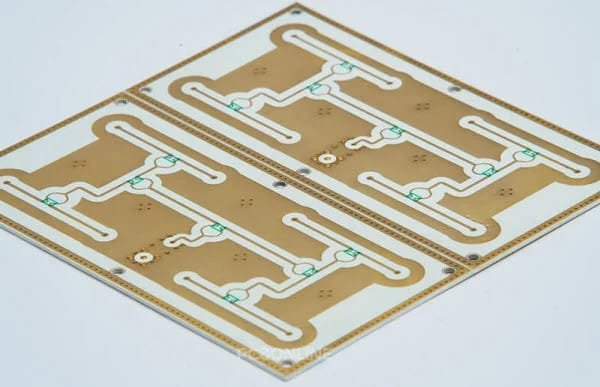
Single Layer Metal Core PCBs - Unmatched Thermal Conductivity
In the realm of high-power electronics and thermal management, single layer metal core PCBs stand out as a specialized solution for dissipating heat efficiently. These unique boards combine the benefits of traditional single-layer circuits with an exceptional metal base, typically aluminum or copper, to create a thermally conductive substrate.
At the core of these PCBs lies a solid metal layer that acts as an integral heat sink. As components generate heat during operation, the metal base rapidly transfers and spreads that thermal load across the entire board surface. This unmatched thermal conductivity eliminates the need for dedicated internal copper layers or complex heat sink designs found in multilayer boards.
The ability to dissipate heat so effectively makes single layer metal core PCBs ideally suited for applications where thermal management is critical. LED lighting systems, power converters, motor drives, and other high-power density electronics can leverage these boards to ensure reliable operation and prevent overheating issues.
In addition to their thermal capabilities, single layer metal core PCBs also offer excellent mechanical strength and rigidity. The solid metal base provides a robust foundation, resistant to vibrations, shocks, and other physical stresses common in industrial environments.
While offering superior thermal performance, these boards do have limitations in terms of component density and routing complexity. With only a single conductive layer, trace routing and component placement must be carefully planned to avoid congestion and maintain signal integrity.
Manufacturers must also consider factors such as insulation resistance, corrosion resistance, and the adhesion strength between the PCB laminate and components during the design and assembly process.
Despite these challenges, the benefits of single layer metal core PCBs often outweigh the drawbacks for thermally demanding applications. Their exceptional heat dissipation capabilities enable more compact and efficient designs, improving product reliability and longevity.
Whether it’s for high-brightness LED arrays, electric vehicle power electronics, or industrial automation systems, single layer metal core PCBs provide a high-performance thermal solution. As technology continues to advance and power densities increase, these specialized boards will play a crucial role in enabling next-generation electronic products to operate within safe thermal limits.

Applications and Advantages of Single Layer PCBs
Single layer PCBs offer an unparalleled combination of simplicity and cost-effectiveness across a diverse range of applications. From rapid prototyping and educational projects to consumer electronics and industrial controls, these versatile boards continue to be an indispensable solution.
In the prototyping realm, single-sided PCBs enable quick design iterations and seamless testing of new concepts. Their straightforward single-layer layout accelerates the manufacturing process by up to 50%, allowing ideas to transition from concept to reality with unmatched speed and agility.
For educational purposes and hobbyist projects, the inherent simplicity of single layer PCBs makes them an ideal learning platform. Students and enthusiasts can grasp the fundamentals of circuit design, assembly, and debugging without the added complexities of multilayer routing. This hands-on experience fosters a deeper understanding and cultivates a passion for electronics.
In consumer electronics, where cost-effectiveness is paramount, single layer PCBs offer a compelling solution. Products like remote controls, smart home devices, and wearable gadgets leverage these boards to achieve manufacturing economies while meeting stringent size and weight constraints. The elimination of complex multilayer stackups results in material savings of up to 30%, directly impacting product affordability.
Moreover, single layer PCBs excel in applications with low to moderate component densities and connectivity requirements. Industrial control systems, automotive electronics, and IoT devices can take advantage of the streamlined single-sided design, reducing complexity without compromising functionality…
Conclusion
Single layer PCBs have cemented their position as a versatile and indispensable component across the electronics landscape. Despite the advancements in multilayer board technology, these single-sided marvels continue to thrive, offering a perfect blend of simplicity, cost-effectiveness, and reliability for a wide array of applications.
From prototyping and educational endeavors to consumer goods and industrial controls, single layer PCBs provide a streamlined foundation for electronic designs with moderate complexity. Their inherent advantages, including ease of manufacturing, compact form factors, and thermal management solutions, make them an ideal choice for power-conscious, space-constrained, or cost-sensitive projects.
At JHYPCB, a leading Chinese PCB manufacturer, we understand the unique requirements of single layer PCB designs. Our comprehensive offering includes single layer rigid boards, flexible circuits, metal core variants, and specialized high-temperature ceramic PCBs. Leveraging advanced manufacturing capabilities and stringent quality controls, we ensure each board meets the highest standards of performance and durability.
Whether you’re a hobbyist exploring the world of electronics, a product developer seeking cost-effective solutions, or an industry leader pushing the boundaries of innovation, JHYPCB is your trusted partner for single layer PCB manufacturing. Embrace the simplicity and versatility of these single-sided boards and unleash your design potential with our expertise and commitment to excellence.
Related Posts
- The Advantages of Double-Sided PCBs for Prototyping
- What is IMS PCB? A Guide to Insulated Metal Substrate PCBs
- Speed Up Your PCB Design with Double Sided Prototyping
- The Many Uses and Benefits of Double-Sided PCBs
- Rigid PCB vs. Flexible PCB: Which is Right for Your Next Project?
- What Are The Types of Metal Core PCBs?
- Key Considerations for Choosing a Reliable Single-Layer PCB Manufacturer
- How Single-Sided PCBs are Made: An In-Depth Look into the Manufacturing Process
- Double Layer PCB: All You Need To Know About These Specially Printed Circuit Boards
- How To Tell single layer PCB From double-sided PCB?
- PCB Layers Explained: Multilayer PCB Stakcup
- What is a printed circuit board (PCB)?












