Flexible Circuit Manufacturing Excellence
High-Quality Double Sided Flex PCB Production
Looking for reliable double sided flex PCB manufacturing services? Our company offers top-quality PCBs with high flexibility, reliability, and cost-effectiveness. Contact us today to learn more!
Leading Double Sided Flexible PCB Manufacturer with Rigorous Quality Control
As a leading double-sided flexible PCB manufacturer in China, JHYPCB takes pride in our rigorous quality control standards and advanced manufacturing capabilities. With over a decade of experience in the PCB industry, we have honed our expertise to deliver superior double-sided flex PCBs that meet the highest quality demands.
Our state-of-the-art facilities are equipped with cutting-edge equipment operated by a team of skilled engineers dedicated to ensuring every double-sided flexible circuit board meets stringent performance and reliability requirements. We adhere to strict ISO-certified quality management processes, from material selection to final testing, to eliminate defects and variations.
What sets JHYPCB apart is our unwavering commitment to quality. We understand that double-sided flex PCBs are critical components in various high-reliability applications, from consumer electronics to aerospace systems. That’s why we go the extra mile to implement comprehensive testing protocols, including electrical, environmental, and flex testing, to validate the functionality and durability of our products.
By choosing JHYPCB as your trusted double sided flexible PCB partner, you can expect superior craftsmanship, competitive pricing, and reliable on-time deliveries – a combination that ensures your projects succeed.
What are Double Sided Flexible PCBs?
Double sided flexible PCBs, also known as double sided flex circuits, are advanced printed circuit boards featuring conductive traces on both sides of a flexible insulating base material. Unlike traditional rigid PCBs, these flexible counterparts boast an impressive ability to bend and conform to various shapes without compromising functionality.
The core of a double sided flex PCB consists of a thin, pliable substrate typically made from polyimide or polyester films. Copper conductors are then applied to both sides of this substrate through an electroless plating process, creating conductive layers for component mounting and interconnections.
One of the key advantages of double sided flexible circuits is their increased routing density and design complexity compared to single-sided flex PCBs. With conductive layers on both sides, designers can achieve higher component integration and more intricate circuitry within a compact footprint, making these boards ideal for applications where space is at a premium.
Moreover, the inherent flexibility of double sided flex PCBs allows them to withstand vibrations, shocks, and repeated bending motions, ensuring reliable performance in dynamic environments. This durability, combined with their lightweight nature, makes them well-suited for applications in industries such as consumer electronics, aerospace, automotive, and medical devices.
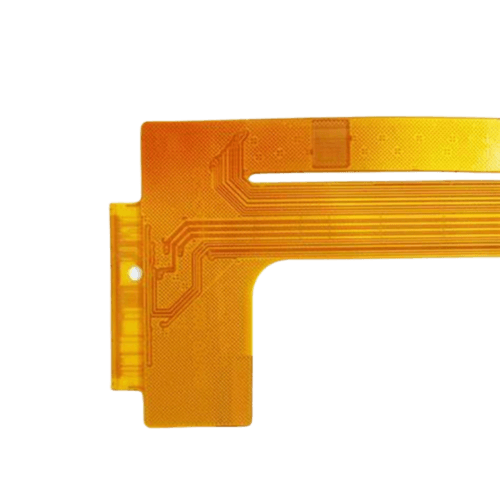
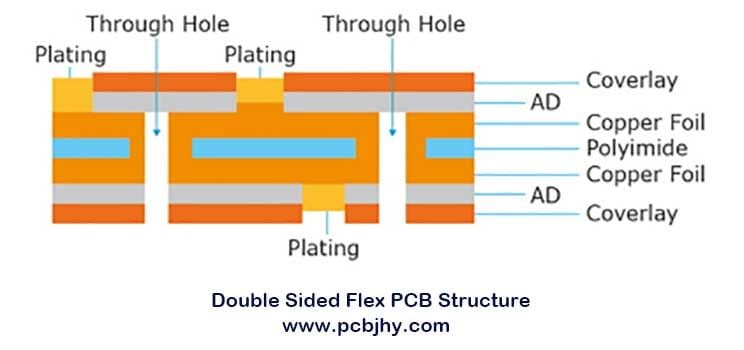
The Advantages of Double-sided Flexible Circuit Boards
At JHYPCB, we leverage our expertise in double sided flexible PCB manufacturing to deliver innovative solutions that meet the demanding requirements of our customers. With a relentless focus on quality, reliability, and customer satisfaction, we strive to be your trusted partner for cutting-edge flex circuit applications.
Space-Saving Design
Double sided flex PCBs are remarkably thin and lightweight, enabling compact designs that maximize available space within the end product, ideal for miniaturized electronics.
Unmatched Durability
The flexible nature of these PCBs allows them to withstand vibrations, shocks, and repeated bending, ensuring reliable operation in the most demanding environments.
Superior Reliability
With precise manufacturing processes, double sided flex PCBs deliver exceptional electrical and mechanical reliability, minimizing failures and downtime.
Versatile Applications
From consumer gadgets to medical devices, aerospace systems to industrial automation, double sided flex PCBs find versatile applications across diverse industries.
High Circuit Density
Conductive layers on both sides enable higher component density and more complex circuitry in a compact footprint, optimizing design capabilities.
Cost-Effective Solution
Despite their advanced features, double sided flex PCBs offer a cost-effective solution compared to rigid boards, maximizing value for your investment.
Types of Double-Sided Flex Circuits
Depending on the circuit design requirements, double-sided flex circuits can be fabricated with a protective layer on a single side, both sides, or neither sides. These flexible circuits are differentiated into categories based on the cover layer and Plated Through Holes (PTH).
- With PTH and Cover layer
- With PTH without a Cover layer
- With a Cover layer, without PTH
- Without PTH or a Cover layer

Applications of Double Sided Flex PCB
Double sided flex PCBs are widely used in various applications that require high flexibility and durability. Here are some examples of the applications of double-sided flex PCBs:
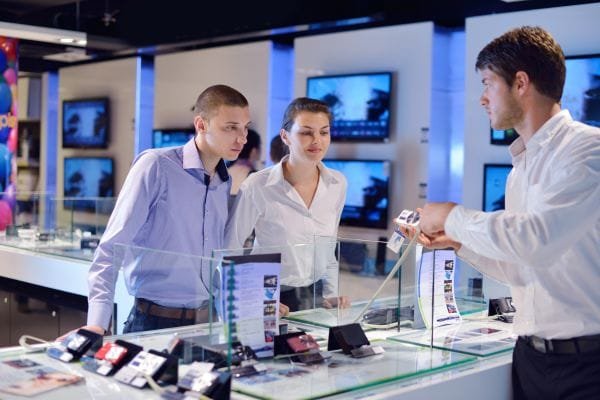

Double-sided flex PCBs are used in smartphones, tablets, wearable devices, and other portable electronics where space is at a premium and the circuit board needs to be flexible to fit into a small form factor.
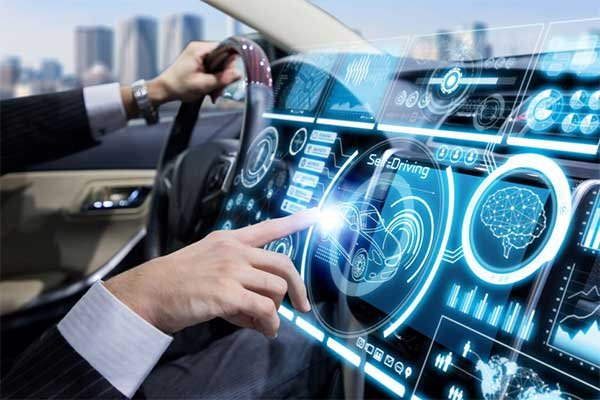

Double-sided flex PCBs are used in automotive electronics such as dashboard displays and infotainment systems. The flexibility of the PCB allows it to bend and conform to the shape of the dashboard or other areas of the vehicle.
Double-sided flex PCBs are used in medical devices such as pacemakers and other implantable devices. The flexibility of the PCB allows it to conform to the body’s shape and reduce the risk of damage or breakage.

Double-sided flex PCBs are used in aerospace and defense systems such as satellites and missile guidance systems. The flexibility of the circuit board allows it to withstand the harsh environmental conditions of space and the battlefield.

Double-sided flex PCBs are used in industrial automation systems such as robots, sensors, and control systems. The flexibility of the circuit board allows it to bend and conform to the shape of the equipment, reducing the risk of damage or breakage.
Double Sided Flex PCB Manufactauring Process
At JHYPCB, we follow a precise and well-controlled manufacturing process to ensure the exceptional quality of our double sided flexible PCBs. Here’s an overview of the key steps involved:
- Substrate Preparation
The process begins with meticulous preparation of the flexible base material, typically polyimide or polyester films. These substrates are carefully cut, cleaned, and inspected to ensure optimal surface conditions for subsequent layers. - Copper Deposition
Next, ultra-thin copper layers are deposited on both sides of the substrate through an electroless plating process. This critical step creates the conductive pathways for circuitry on the double sided flex PCB. - Photolithography
A photosensitive material is then applied and selectively exposed to UV light through a circuit pattern photomask. This step defines the precise traces and pad locations on the copper layers. - Etching
The exposed areas of the copper are subsequently removed through a chemical etching process, leaving behind the desired circuit pattern on both sides of the flexible substrate. - Hole Drilling
Precise drilling or punching is performed to create vias and other necessary holes for component mounting and layer interconnections. - Plating and Surface Finishes
Additional metal plating and surface finishes like ENIG, HASL or OSP are applied to enhance solderability, conductivity, and protective properties of the double sided flex PCB. - Solder Mask and Legend
A solder mask is carefully applied to protect the copper traces, while legends are printed for component identification and reference designators. - Final Assembly and Testing
The last step involves assembling components on the double sided flex PCB, followed by comprehensive electrical testing, environmental stress screening, and final quality inspection.
Throughout this intricate process, we maintain stringent quality control measures, from raw material inspection to in-process monitoring and final testing. Our manufacturing expertise ensures consistent quality and reliable performance of the double sided flexible circuits we produce.
Testing Methods for Double Sided Flex PCB
Testing double-sided flex PCBs is an essential part of the manufacturing process to ensure the quality and reliability of the final product. Here are some of the most common testing methods for double-sided flex PCBs:
Electrical testing
Electrical testing involves applying a voltage to the circuitry and measuring the current and resistance of the traces and components. This can detect any open or short circuits, as well as other defects such as improper component values or incorrect polarity.Continuity testing
Continuity testing is used to verify that there is a connection between two points in the circuit. This is typically done using a multimeter to check for resistance or voltage across the circuit.Thermal testing
Thermal testing is used to determine how well the double-sided flex PCB handles heat. This can involve applying a controlled amount of heat to the board and measuring the temperature, or exposing the board to a temperature chamber to simulate the conditions it will be exposed to in its intended application.Vibration testing
Vibration testing involves subjecting the double-sided flex PCB to mechanical vibrations to simulate the conditions it will be exposed to during use. This can detect any weak or damaged areas in the circuitry or components.Flex testing
Flex testing involves bending or flexing the double-sided flex PCB to test its durability and resistance to mechanical stress. This can be done manually or using a specialized testing machine that applies controlled amounts of stress to the board.Environmental testing
Environmental testing involves exposing the double-sided flex PCB to different environmental conditions such as temperature, humidity, or chemicals to test its resistance to these conditions. This can help detect any weaknesses in the circuitry or components that may affect performance or reliability.
Trusted Flex PCB Manufacturer
We are a reliable manufacturer and supplier of flex PCBs, offering high-quality solutions for single-sided, double-sided, and multi-layer flex PCB prototyping and volume production, as well as flexible PCB assembly services to meet our customers’ diverse needs.
As a trusted flex PCB manufacturer and supplier, we are committed to providing our customers with quality products and services. We have a professional R&D and production team that uses advanced manufacturing technology and equipment to ensure our products meet customers’ requirements and standards. Our quality management system is strictly managed according to ISO standards to ensure stable and reliable product quality.
If you are looking for a reliable flex PCB manufacturer and supplier, please feel free to contact us. We will provide you with quality products and services to meet your different needs.
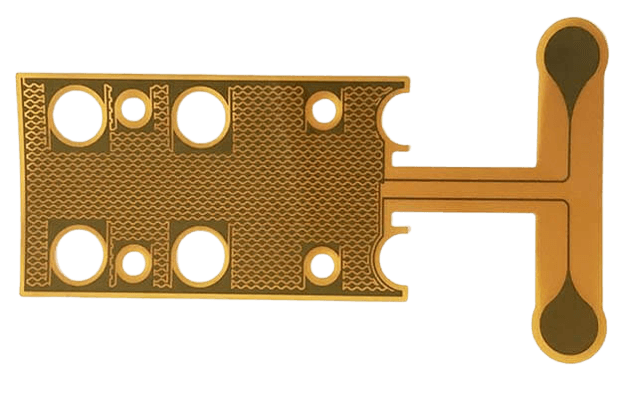
Why Choose JHYPCB for Your 2 Layer Flexible PCB?
Years of experience
JHYPCB has been in the PCB industry for over 10 years, with extensive knowledge and experience in manufacturing double-sided flex PCBs.
Quality
JHYPCB uses high-quality materials and advanced manufacturing processes to ensure that double-sided flex PCBs meet the highest quality standards.
Cost-effectiveness
JHYPCB offers competitive pricing for their double-sided flex PCBs, without sacrificing on quality.
Customization
JHYPCB offers a wide range of customization options for double-sided flex PCBs, such as shape, size, and thickness, to meet the specific needs.
Reliable delivery
JHYPCB has a strong track record of delivering double-sided flex PCBs on time and with reliable shipping options to ensure that your order arrives when you need it.
Double Sided Flex PCB Manufacturing Capabilities
| Manufacturing Capability | Details |
|---|---|
| Materials | Polyimide (PI) and polyester (PET) films |
| Layers | Up to 4 layers |
| Copper Weight | Standard copper weight for double-sided flex PCBs is 1oz (35 µm) |
| Minimum Trace/Space | 3 mil (0.076 mm) |
| Minimum Hole Size | 0.2 mm (8 mil) |
| Surface Finish | HASL, ENIG, OSP, immersion silver, and gold plating |
| Solder Mask | LPI solder mask in various colors |
| Silkscreen | White or black silkscreen |
| Maximum Panel Size | 457 x 610 mm (18 x 24 inches) |
| Quality Standards | Manufactured according to IPC Class 2 or Class 3 standards |
| Testing | Electrical testing, impedance testing, and other tests as per customer requirements |
Note: These are general capabilities and may vary depending on specific customer requirements and project specifications. Please contact us for more information on our double-sided flex PCB manufacturing capabilities.
FAQs for Double Sided Flex PCB
What is a double-sided flex PCB?
A double-sided flex PCB is a type of flexible printed circuit board that has conductive traces on both sides of the substrate, allowing for increased circuit density and routing flexibility.
What are the advantages of double-sided flex PCBs?
Double-sided flex PCBs offer increased routing flexibility and component density, as well as improved reliability and durability compared to rigid PCBs.
What materials are used to make double-sided flex PCBs?
The most common materials used for double-sided flex PCBs are polyimide (PI) and polyester (PET) films.
What is the maximum number of layers for double-sided flex PCBs?
Double-sided flex PCBs can have up to four layers.
What is the minimum trace/space for double-sided flex PCBs?
The minimum trace/space for double-sided flex PCBs is typically 3 mils (0.076 mm).
What is the minimum hole size for double-sided flex PCBs?
The minimum hole size for double-sided flex PCBs is typically 0.2 mm (8 mils).
What surface finishes are available for double-sided flex PCBs?
Common surface finishes for double-sided flex PCBs include HASL, ENIG, OSP, immersion silver, and gold plating.
What testing methods are used for double-sided flex PCBs?
Electrical testing and impedance testing are commonly used for double-sided flex PCBs. Additional testing may be performed as per customer requirements.
What quality standards do double-sided flex PCBs meet?
Double-sided flex PCBs are manufactured according to IPC Class 2 or Class 3 standards, depending on the customer's requirements.
Double-Sided Flex PCB vs. Single-Sided Flex PCB: What are the differences?
The main difference between double-sided and single-sided flex PCBs is the number of conductive layers they have. A single-sided flex PCB has only one layer of conductive material, while a double-sided flex PCB has two. This allows for more complex circuit designs and a greater density of components on double-sided flex PCBs. Double-sided flex PCBs are also more versatile, as components can be surface-mounted on either side of the board, while single-sided flex PCBs typically only have surface-mounted components on one side. However, single-sided flex PCBs are often simpler and less expensive to manufacture than double-sided flex PCBs.
Double-Sided Flex PCB vs. multilayer Flex PCB: What are the differences?
Double-sided flex PCBs have two layers of conductive material, while multilayer flex PCBs can have three or more layers. The primary difference between the two is the complexity of the circuit design that can be achieved. Multilayer flex PCBs allow for more complex circuitry and more components to be packed into a smaller space, resulting in improved functionality and performance. Double-sided flex PCBs are less complex than multilayer flex PCBs, but they are still a good choice when a circuit needs to be more compact than can be achieved using a single-sided flexible PCB.
However, multilayer flex PCBs are generally more difficult and expensive to manufacture than double-sided flex PCBs due to the precise alignment required to stack the layers together. The additional layers can also make the board thicker and less flexible overall. Combining multiple designs into a single, multilayer PCB can be a cost-effective solution for more complex designs, but it requires careful consideration of floor planning and signal integrity.
What types of components can be used with a double-sided flex PCB?
Double-sided flex PCBs can be used with a wide range of electronic components, including surface mount components, through-hole components, and flip-chip components.
Explore Our PCB Fabrication Services
Related Reading
- What are the Different Types of Flexible Circuits?
- What are the Materials for Flex Circuits?
- Flexible PCBs: Advantages And Disadvantages
- Comprehensive Guide to Manufacturing Flex PCB with Stiffener
- The Ultimate Guide to Flex PCB Stiffener
- Flexible PCB Pricing: Factors, Trends, and Cost-Saving Strategies
- Pressure Sensitive Adhesive (PSA) for Flex and Rigid-Flex PCB
- EMI Shielding Film In FPC Applications