LED PCB Manufacturing Service
Custom LED PCB Manufacturing Services
As a PCB manufacturer with more than 10 years of experience, we can provide LED PCB manufacturing service, components sourcing, and assembly.
Your trusted LED PCB manufacturer
JHYPCB is a leading printed circuit board manufacturer based in China. With over 15 years of experience in the PCB industry, we specialize in manufacturing high-quality and cost-effective PCBs.
Our capabilities cover the entire PCB production process, from prototype to high-volume fabrication. We are especially adept at manufacturing LED PCBs and providing LED PCB assembly services.
At JHYPCB, we leverage the latest technologies and engineering expertise to fabricate complex LED PCBs. Whether it’s simple double-sided boards or advanced multilayer LED boards, we can handle it. From materials selection and layer stacking to final finishes, our engineering team ensures your LED PCBs meet all mechanical, thermal, and electrical requirements.
For LED PCB assembly, we have robust surface mount technology (SMT) lines to assemble tiny LED components onto the boards accurately. With automated optical inspection (AOI), we guarantee the LEDs are precisely placed as per your design. During assembly, we also perform comprehensive testing and quality checks to ensure your finished boards function flawlessly.
Over the years, JHYPCB has supplied LED PCBs for customers across consumer electronics, automotive, industrial equipment, and many other industries. We are committed to delivering high-quality solutions on time with cost-effective and flexible options. Contact us today to learn how our LED PCB fabrication and assembly services can benefit your next project!

What is LED PCB?
LED PCBs are a unique set of printed circuit boards that are purposely designed for use in a wide range of lighting applications and modules. These PCBs involve the mounting of several lighting-emitting diodes (LEDs) onto a PCB. When the LEDs are mounted onto the PCB, this forms a complete circuit. This way, the behaviour of the LEDs can be controlled fully by using various types of switches or chips.
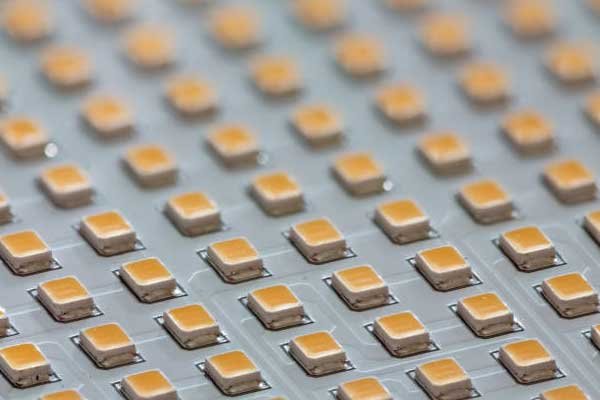

LED PCB Manufacturing Capabilities
At JHYPCB, we have extensive capabilities to fabricate all kinds of LED printed circuit boards.
Types of LED PCBs:
- Flexible LED PCBs – We manufacture single, double, and multilayer flex LED boards using polyimide and other flexible substrate materials. Ideal for applications requiring dynamic shaping and bending.
- Rigid LED PCBs – We offer rigid FR4 boards as well as advanced substrates like aluminum and metal core for superior thermal performance. Support for 2-layer up to 12+ layers.
LED Packages Supported:
- SMT LEDs – We assemble chip-on-board and all kinds of surface-mount LED components.
- COB LEDs – Chip-on-board LED arrays and modules can be directly soldered onto the PCB.
- Through-hole LEDs – We can assemble simple through-hole LEDs as well as arrays.
Materials and Layer Counts:
- FR4, Aluminum, Ceramic, Teflon, and other substrate materials.
- 2-layer boards up to 12+ layers or more – we fabricate complex multilayer LED PCBs.
PCB Size and Thickness:
- Board sizes from small prototypes to large panels.
- Thickness from 0.4mm to over 2mm.
Finishes:
- Immersion Silver, Immersion Gold, Immersion Tin, OSP, Hard Gold, HASL and more.
We also perform SMT assembly, AOI inspection, and reliability testing in-house to deliver complete LED PCB solutions. Our engineering team provides full support to manufacture your LED boards reliably and efficiently.
GET A FREE QUICK QUOTE.
Why Choose JHYPCB?
There are many reasons to choose JHYPCB as your LED PCB partner:
- One-Stop Service: We provide a comprehensive solution including PCB fabrication, SMT assembly, testing, and quick turnaround delivery. You don’t need to source different suppliers.
- Cost Competitive Pricing: By optimizing our manufacturing processes, we offer very competitive pricing without compromising on quality.
- Fast Turnaround Time: Our streamlined workflows allow us to deliver LED PCB prototypes in as fast as 24 hours and production orders in 2-4 days.
- Engineering Support: Our team of PCB engineers provides invaluable guidance at every step – from design review to fabricating your optimized boards.
- Quality: We follow strict quality control protocols and inspections at every stage of LED PCB production. This results in high yields and reliable boards.
- Long-Term Partnership: We focus on developing strategic win-win partnerships with customers for continuous collaboration.
- Convenience: It is easy to get quotes, order online, and get quick feedback from our engineers through multiple channels.
With countless LED PCBs delivered, we have the experience and capabilities to manufacture boards that meet your requirements on time. Contact us today to discuss your project and we will respond with competitive quotes quickly.

What is SMD in LED PCB?
SMD (Surface Mount Device) technology is widely used in LED PCB manufacturing due to its many advantages over through-hole components. SMD components are smaller, lighter, and require less space, making them ideal for use in LED PCBs where space is often limited. Additionally, SMD components can be placed on both sides of the PCB, allowing for more compact designs and greater flexibility in circuit layout.
In LED PCBs, SMD components such as resistors, capacitors, and diodes are commonly used in conjunction with LED chips to create compact and efficient lighting systems. These components are mounted directly onto the surface of the PCB using automated pick-and-place machines, which ensure precise component placement and high-speed production.
SMD technology also allows for greater precision in LED PCB manufacturing, as the components are mounted using solder paste and reflow soldering techniques, which create a more reliable and durable connection between the component and the PCB.
Overall, the use of SMD technology in LED PCB manufacturing provides many benefits, including increased space efficiency, improved precision, and higher production speeds, making it an essential component in the design and manufacture of modern LED lighting systems.
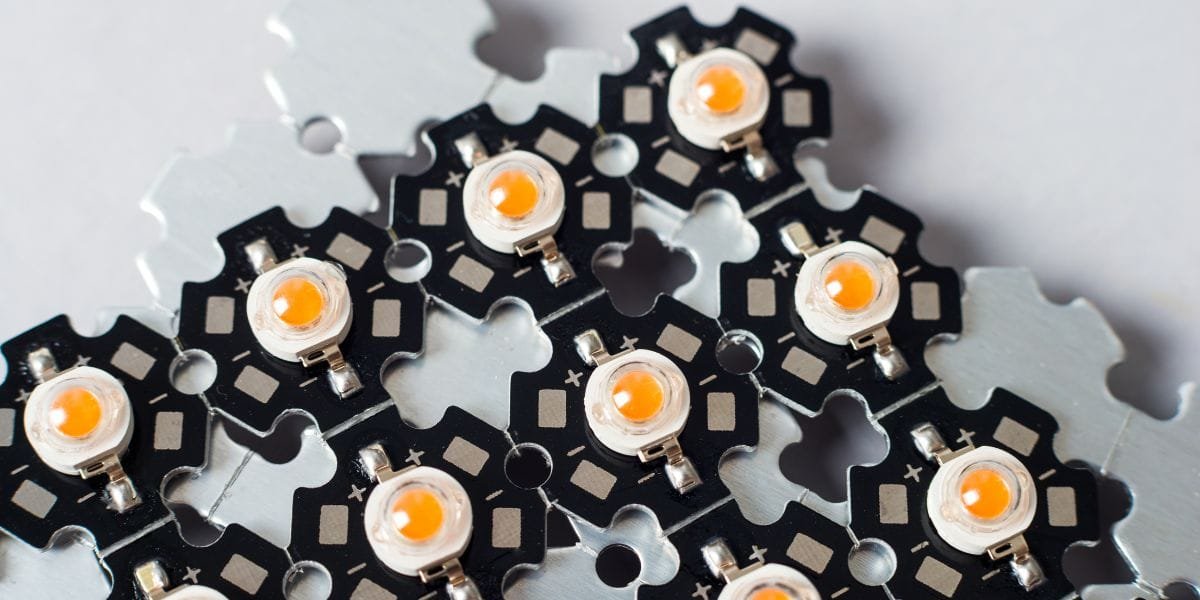

Factors to Consider When Design an LED PCB Board
Designing an LED PCB involves considering several important factors to ensure that the final product meets the required specifications. The following are the key factors that should be considered when designing an LED PCB:
- LED Type and Configuration: The first factor to consider is the type and configuration of the LED. This includes factors such as the color, brightness, and power rating of the LED, as well as the number and placement of the LED chips on the PCB.
- Materials: Materials used for the LED PCB board should work together to remove and dissipate extra heat, insulate conductors, and allow electrical connections between LED components. The base layer for many LED circuit boards uses aluminum. Over the aluminum base is the dielectric layer, topped by the copper circuit layer and the solder mask. This type of structure also goes by the term insulated metal substrate (IMS). The aluminum base works well to release extra heat and assist in thermal management.
- Thermal Management: LED chips generate heat during operation, and it is important to design the PCB to dissipate this heat effectively. Factors to consider include the size and shape of the PCB, the placement of thermal vias, and the use of heat sinks or other cooling mechanisms.
- Power Supply: The power supply is a critical component in LED PCB design, as it must provide a stable and consistent voltage to the LED chips. Factors to consider include the voltage and current requirements of the LED chips, the type of power supply (AC or DC), and the efficiency of the power supply.
- Circuit Layout: The circuit layout is an important factor in LED PCB design, as it determines the overall functionality and performance of the PCB. Factors to consider include the placement and routing of components, the use of ground planes and power planes, and the placement of decoupling capacitors.
- Environmental Factors: LED PCBs may be subjected to various environmental factors, such as temperature, humidity, and vibration, which can affect their performance and longevity. It is important to consider these factors during the design process and select materials and components that can withstand these conditions.
- Manufacturing Requirements: Finally, LED PCB design should consider the manufacturing requirements, such as the capabilities of the manufacturer, the cost and availability of materials and components, and the desired production volume.
- Surface Finish: The surface finish of an LED PCB is a crucial aspect of its manufacturing process, as it affects the quality and reliability of the board. There are several surface finishes available for LED PCBs, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. Some common surface finishes used in LED PCB manufacturing include HASL (Hot Air Solder Leveling), ENIG (Electroless Nickel Immersion Gold), OSP (Organic Solderability Preservatives), Immersion Tin, and Immersion Silver.

Get an accurate quote for your LED PCB projects
If you need us to send your accurate and affordable quotations about our innovative LED PCBs, you can simply fill in the form. Use the featured request form on the website to get the right quotations to form your LED PCB projects. Our team of experts will know how our products will fit easily into your projects. We offer first-class LED PCB assembly and fabrication services for our customers. To get more information about LED PCB services and products, you can send us an email at sales@pcbjhy.com. The phone is also available via phone on +86 13825274100.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is an LED PCB?
An LED PCB is a type of printed circuit board specifically designed for LED lighting applications. It provides a platform to mount and connect LED components to form a lighting system.
How does an LED PCB differ from a traditional PCB?
LED PCBs have unique features and requirements that differentiate them from traditional PCBs. For example, they need to dissipate heat effectively, and they require specialized layouts for optimal performance.
What types of LED PCB materials are available?
Common LED PCB materials include aluminum, copper, and FR4. The material used depends on the specific application and performance requirements.
What is the best material for an LED PCB?
The best material for an LED PCB depends on the specific application and performance requirements. However, aluminum is often used due to its excellent thermal properties.
What is the expected lifespan of an LED PCB?
The lifespan of an LED PCB depends on various factors, such as the quality of the materials used, operating conditions, and maintenance practices. Typically, an LED PCB can last anywhere from several years to decades.
What is the cost of an LED PCB?
The cost of an LED PCB depends on several factors, such as the size, complexity, and material used. Generally, LED PCBs are more expensive than traditional PCBs due to their specialized requirements.
What are the types of LED PCB?
The main types of LED PCBs are:
- Single-sided LED PCBs
- Double-sided LED PCBs
- Multilayer LED PCBs
- Flexible LED PCB Strips
These are the most common LED PCB variants seen in practical applications. As an LED PCB manufacturer, we primarily manufacture single-sided, double-sided, and multilayer rigid LED boards, but can also produce flexible LED PCB strips.
What are the benefits of LED lighting?
Here are some of the key benefits of LED lighting:
- High energy efficiency - LEDs convert over 80% of energy into light vs only 10-20% for incandescents. This saves electricity.
- Long lifespan - LEDs can last over 50,000 hours compared to 1,000 for incandescents. Less frequent replacement needed.
- Durable - LEDs have no filaments or glass bulbs to break. Making them withstand shock/vibration.
- Cool operation - LEDs produce minimal heat, reducing cooling requirements.
- Compact size - Small LEDs allow flexible and innovative lighting fixture designs.
- Fast switching - LEDs can turn on/off instantly, allowing dynamic control.
- Reliable performance - LED light output and color is consistent over time.
- Environmentally friendly - LEDs contain no mercury or toxic materials.
In summary, LED lighting delivers significant energy, maintenance, and performance advantages over traditional lighting. The long lifespan and reliability make LEDs ideal for sustainable and smart lighting applications.
What are the advantages of LED PCB?
Here are some key advantages of using LED PCBs:
- Effective heat dissipation - The metal core or substrate in LED PCBs conducts heat away from the LEDs preventing overheating.
- Higher light density - LED PCBs allow mounting LEDs in a dense configuration leading to brighter light output.
- Reliability - The PCB provides a robust base for securely mounting LED components.
- Design flexibility - PCBs allow creating customized LED arrays and form factors.
- Simplified assembly - Automated SMT assembly can be used to populate LED PCBs improving efficiency.
- Cost-effectiveness - PCB manufacturing allows producing LED boards economically in high volumes.
- Easy integration - LED PCBs can be easily integrated with heat sinks, lenses and other optics.
- Consistent performance - The PCB substrate ensures all LEDs maintain the same orientation and characteristics.
- Long lifespan - PCBs are durable and protect LEDs from damage due to shocks and vibration.
In summary, LED PCBs enhance thermal performance, reliability, design flexibility and manufacturing efficiency compared to simple LED arrays or individual LED components.
What are the applications of LED PCB?
Here are some of the main applications where LED PCBs are used:
- LED Lighting - LED PCBs are commonly used in LED bulbs, tubes, panels, street lights, automotive lighting etc.
- Backlighting - LED backlights using PCBs are found in devices like TVs, monitors, displays, and signage.
- Grow Lights - LED grow lights use PCBs to hold multiple high power LEDs.
- Decorative Lighting - PCBs allow creating LED strips and other decorative lighting effects.
- Medical Devices - LED PCBs provide illumination for medical devices like microscopes and surgical equipment.
- Automotive Lighting - Interior and exterior automotive lights like headlights and tail lights employ LED PCBs.
- Electronic Devices - Small LED indicator lights on devices like routers, modems, appliances etc often use simple PCBs.
- AV Equipment - LED PCBs are used to provide display backlighting and indicator lights on AV devices.
- Wearables - Flexible LED PCBs allow creating illuminated clothing, safety vests, bands etc.
In summary, LED PCBs serve as the foundation for implementing LED lighting and illumination across diverse applications, from home to industry.

Related Reading
- Achieve Customized Flexible Lighting with LED Strip PCBs
- Achieve Design Freedom with Flexible LED PCBs
- LED PCB Design Guide: Tips and Best Practices for Manufacturers
- The Best Materials for LED PCB Boards
- Expand Your LED Lighting With Custom LED PCBs
- China’s Leading Manufacturer and Assembler of LED PCBs
- What is IMS PCB? A Guide to Insulated Metal Substrate PCBs
- SMT Vs. SMD: Understanding The Key Differences
- SMT Assembly Vs. THT Assembly: What Is The Difference?